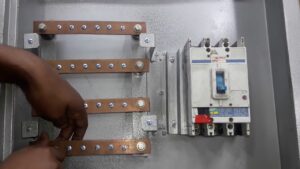
Busbars, the unsung heroes of the electrical industry, are fundamental to any power distribution unit. This article delves deep into what busbars are, their types, selection criteria, and their role in the electrical industry. Let’s begin!

What is a Busbar?
A busbar, often referred to as a bus, is a conductor that connects various current-blocking branch circuits in an electrical installation. Acting as a carrier, it collects and distributes electricity. These conductors are critical in each power distribution unit as they collect, distribute, and transmit electrical energy.
Given the massive amounts of electric energy they handle, busbars are subject to substantial heating and electrodynamic effects, especially during short circuits. Consequently, choosing the suitable busbar material, cross-sectional shape, cross-sectional area, and perfect busbar bending machine is critical to ensure safe and economical operation.
Types of Busbars
There are two commonly used types of busbars: hard busbars and soft busbars.
Hard Busbars
Hard busbars are typically made of copper or aluminum and come in rectangular, trough, and tubular shapes. They’re primarily used in indoor power distribution devices of 35 kV and below. Outdoor power distribution devices of 110 kv and 220 kv sometimes use aluminum tube bus bars.
Soft Busbars
Soft busbars, on the other hand, include aluminum-stranded wires, copper-stranded wires, or steel-core copper wires. These are mainly used for outdoor power distribution devices above 35 kv.

Busbar Selection and Application
Different environmental conditions call for varying types and materials of busbars.
Selecting the Busbar Cross-Section
The busbar cross-section should be selected based on the maximum long-term operating current. It should also be verified for short-term thermal and dynamic stability under a maximum short-circuit current condition.
Thermal Stability of the Busbar
During a short circuit, a large amount of heat can’t be dissipated into the surrounding air quickly enough, causing the temperature of the conductor to rise rapidly. The allowable heating temperatures of copper and aluminum bare busbars when short-circuited are 300° and 200°, respectively.
Dynamic Stability of the Busbar
When a short circuit occurs, a significant impact current flows through the busbar, generating immense electric power. If the mechanical strength of the busbar and pillar insulators is insufficient, deformation or damage may occur.
Conclusion
To sum up, busbars are crucial components in power distribution units. They perform the essential tasks of collecting, distributing, and transmitting electrical energy, serving as the foundation of our electrical power systems. By familiarizing ourselves with the various types of busbars and their applications, we can maximize their effectiveness for safe and efficient operation in diverse environments.
FAQs About Busbars
What is a busbar?
A busbar is a conductor that connects various current-blocking branch circuits in an electrical installation. It collects and distributes electricity.
What are the types of busbars?
There are two main types of busbars: hard busbars and soft busbars.
What materials are used to make busbars?
Hard busbars are typically made from copper or aluminum, while soft busbars can be made from aluminum-stranded, copper-stranded, or steel-core copper wires.
How is the cross-section of a busbar selected?
When selecting the cross-section of a busbar, it’s crucial to consider both the maximum long-term operating current and verify its short-term thermal and dynamic stability under maximum short-circuit current conditions.
How can the stability of a busbar be increased?
To improve busbar stability, several measures can be taken. Firstly, reducing the distance between supporting insulators of the same phase busbar will help improve stability. Secondly, increasing the distance between busbar phases is another effective method. Lastly, it is essential to limit short-circuit currents to enhance overall stability.