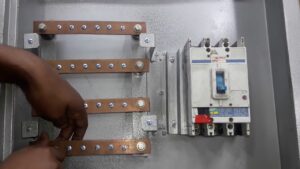
A bus bar is an essential component of electrical distribution systems. Simply put, a bus bar is a conductor that serves as the central hub for distributing power from an incoming source to multiple outgoing electrical circuits or devices. But what exactly is a bus bar, and why is it so crucial in various electrical applications? As a professional bus bar machine manufacturer, I wrote this guide to share all you need to know.

What is a Bus Bar?
Before getting into the intricacies, let’s start with the fundamentals – what is a bus bar?
In electrical engineering terminology, a bus bar refers to a metallic strip, bar, tube, or rod that conducts current from one location to another. Bus bars feature a robust construction, typically using highly conductive metals like copper or aluminium. They often sport an uninsulated design to enable heat dissipation through exposed surfaces.
Now, you may wonder – how does a simple metal bar help transmit electricity so efficiently?
The key lies in their exceptional current carrying capacity, far greater than regular wires or cables. Bus bars achieve this due to their:
- Substantial cross-sectional area
- Shorter current path
- Minimal resistance
These attributes combine to create a low impedance path for current to flow smoothly across the bus bar system.
The Purpose of Bus Bars
So why use bus bars instead of traditional wires or cables? What role do they serve in electrical frameworks?
The principal functionality of bus bars includes:
- Centralised power distribution
- Easy system expansion/modification
- Minimal transmission losses
- Enhanced safety
- Simplified design
Centralized Power Distribution
Bus bars offer a neat, orderly solution for distributing power, consolidating a number of electrical connections into a common point or strip. This beats the complexity of masses of cables that easily turn into “spaghetti junctions”.
Easy System Scalability
The modular bus bar design allows additional loads and electrical equipment to be conveniently added. For instance, tapping a new circuit from a main bus bar proves quick and uncomplicated.
Lower Transmission Losses
Owing to the short distance between connected equipment, bus bars enable efficient delivery of electrical power with marginal energy losses along the way.
Improved Safety
With all electrical links converging at an accessible bus bar, integrating protective devices like fuses and circuit breakers becomes simpler. This beefs up the overall system safety.
Streamlined Design
Bus bars lend themselves seamlessly to structured wiring schemes in switchgears, control panels and distribution boxes. This orderly layout then assists maintenance and troubleshooting.
Classification of Bus Bars
Not all bus bars are created equal. Based on different design aspects, we can categorize them into several key types:
By Material
Copper: With exceptional conductivity only second to silver, copper makes for the most preferred bus bar material, specifically in low voltage settings below 1000V. Some other benefits include malleability, corrosion resistance and durability.
Aluminium: Aluminium proves a lighter and cheaper alternative to copper bus bars. But the tradeoff is marginally lower conductivity coupled with a larger size to carry the same current as a copper bus bar. Aluminium bus bars find widespread application in high voltage systems above 1000V.
Brass and Bronze: Brass and bronze bus bars feature
attributes intermediate between copper and aluminium. However, the biggest disadvantage remains their high cost, limiting their application.
By Shape/Profile
Rigid bus bars: These simple aluminum or copper bars represent the standard variety, tailored to handle high loads in a compact footprint. Robust mechanical strength marks another plus.
Flexible bus bars: Built from layered flat copper strips, flexible bus bars balance adequate current capacity and a slender, pliable form. This suits applications requiring bus bars to undergo frequent reconfiguration.
Hollow bus bars: As the name indicates, a tubular or hollow cross-section allows substantial current flow in a lightweight package ideal for high-power density applications.
By Orientation
Vertical bus bars: This setup serves frequently accessed low voltage switchgear in commercial buildings and UPS systems where height proves limited. Allows tap-off connections from the sides.
Horizontal bus bars: In high voltage gear, a horizontal layout better dissipates heat while allowing tap connections from above. Takes up more floor space.
L-shaped/T-shaped: Industrial switchboards often utilize L-shaped or T-shaped bus bars to optimize space and access in all directions.
Practical Applications of Bus Bars
Now that we have built a sound understanding of what bus bars are, let us explore some common real-world applications leveraging bus bar systems:
Low Voltage Switchgear
In electrical distribution systems across residential, commercial and industrial facilities, bus bars constitute crucial components. You will usually find them enclosed in grounded metal cabinets also housing protective and switching apparatus like circuit breakers, fuses and isolators.
UPS Systems
Uninterruptible Power Supply or UPS systems utilize bus bars for efficient distribution of backup power to mission-critical loads like data centers and medical equipment. Reliable high-current connections become imperative in these contexts.
Battery Banks
Owing to their high-current capacity and lightweight construction, bus bars serve as the optimal approach to interconnect cells in battery banks found in electric vehicles, data centers and power backup systems.
Alternators & Generators
In gensets and alternator assemblies, manufacturers invariably deploy bus bars for collecting the electrical output and transmitting it downstream to other devices. Robustness and minimal power loss hold equal importance here.
Electrical Control Panels
Within motor control centers and PLC/relay control panels, equipment often taps power from bus bars instead of point-to-point wiring. This tidy scheme shrinks panel footprint and simplifies interconnections.
Why Choose Bus Bars Over Cables?
Cables and bus bars represent two alternative technologies for power transmission in electrical systems. But what makes bus bars frequently preferred?
Higher Current Ratings
Bus bars easily outclass regular cables when it comes to current capacity. For the same cross-section and voltage grade, a bus bar proves capable of allowing a substantially higher current flow.
Lower Impedance
Greater surface area and shorter path translates to lower impedance for bus bars compared to cables. This further squeezes power losses stemming from resistive components.
Enhanced Safety
The uninsulated metallic construction of bus bars stays shielded within properly earthed electrical enclosures for accident prevention. Cables, however, remain continually exposed in conduits.
Tidier Installation
Cables generally occupy considerable space with complex wiring schemes. Bus bars offer cleaner, systematic architecture by unifying electrical nodes. This also aids future troubleshooting.
Easier Maintenance
Rigid bus bars rarely incur physical damage or deterioration unlike cables prone to cuts, abrasion, kinks and moisture ingress. Connections also hold fast avoiding periodic tightening.
Lower Cost
For equivalent load applications, bus bars achieve substantial cost savings over cables owing to the economy of conductor material and simplicity of connections. This gap further widens as system capacity increases.
In a nutshell, bus bars triumph over traditional wiring solutions on multiple counts – safety, longevity, ease of modification and sheer performance. Of course, either may be alternatively selected based on design constraints and techno-economic factors.
To Wrap Up..
A bus bar epitomizes efficient power distribution in electrical engineering, serving as a robust conductive backbone that feeds various downstream components. Its virtues include high current capacity, minimal losses, straightforward integration, safety and simplified maintenance.
Common household devices like circuit breaker panels, UPS systems and EV charging stations all harness bus bars due to their exceptional dependability and safety. On a broader scale, they also enable the bulk transmission of electricity across vast distances up to hundreds of kilometers.
So next time you come across an electrical cabinet or a EV battery pack brimming with orderly metal strips, you can be certain those are ingenious bus bars in action!