Busbars, the unsung heroes of the electrical world, often find their way into many applications where efficient power distribution is crucial. If you’ve ever wondered whether you need one or want to delve deeper into their significance, this article has you covered.
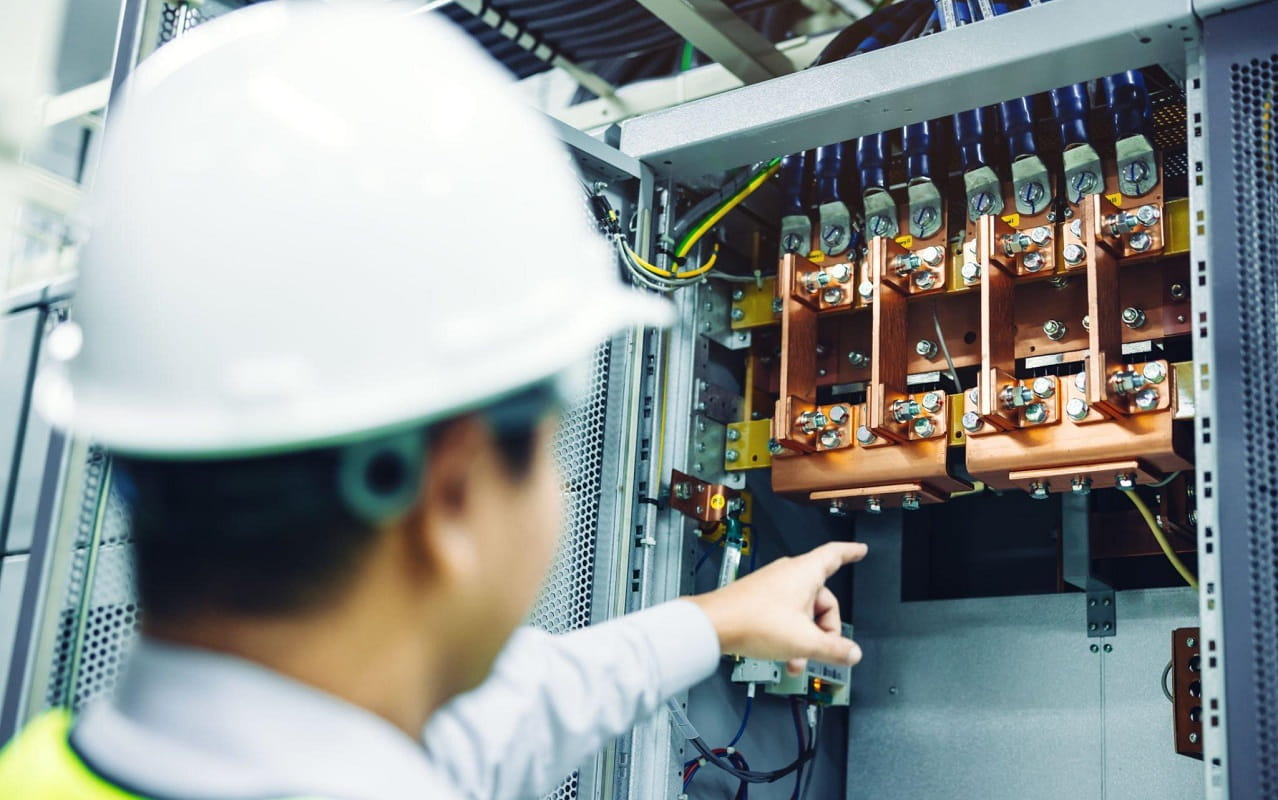

What is a Busbar?
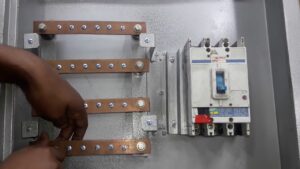
A busbar, an integral component in the electrical industry, is a conductive strip typically crafted from copper or aluminum. Its primary function? Connect and unify lines with the same voltage within power distribution panels, boxes, and substations. A busbar’s thickness, or cross-sectional area, is pivotal: it dictates the safe current flow. While some busbars might be as slender as 10 square millimeters, it’s not uncommon to find substations harnessing beefy metal rods boasting a diameter of 50mm or more to serve as their connecting powerhouse. A busbar is a bridge ensuring smooth electric connectivity in power systems.
Common Applications of Busbars
Busbars are versatile components with critical roles in various applications across many sectors.
- Switchgear: Busbars are often used as a central hub to connect high-voltage equipment in switchgear systems. Housed typically within switchgear panel boards, they carry and distribute current power effectively across all related electrical devices.
- Panel Boards: They are essential components within panel boards, playing a crucial role in current power distribution. The primary function of busbars in this setting is to establish an electrical connection point for incoming and outgoing circuits.
- Power Distribution Units (PDUs): Busbars are integrated into PDUs to facilitate efficient power transfer and distribution. They allow current branching off at any point, providing built-in flexibility for power distribution. This capability is especially beneficial in dense infrastructures, where dynamic power requires a versatile distribution model.
- Battery Banks: In battery banks, often found in electric and hybrid vehicles, busbars offer an effective solution for low-voltage equipment connection. Their application in battery banks ensures efficient power links for generators, transformers, and charging stations, where flexible connectivity is paramount.
The Advantages of Using a Busbar
Understanding the tangible benefits of busbars makes their necessity clear.
1. Cost-Effective Solution
Laminated Bus Bars Minimize Manufacturing Expenses
Rather than an extensive array of individual wires, busbars utilize laminated constructions that streamline the assembly process. This not only slashes assembly time but also reduces material handling overheads. Furthermore, having predetermined conductor termination points rids the need for guesswork during assembly.
Simplified Inventory Management
A busbar system invariably means fewer components. The result? A simplified procurement process, reduced inventory costs, and efficient material handling.
2. Customization for Maximum Efficiency
Tailored to Your Needs
Every electrical system is unique. Fabricated busbars can be customized to meet specific requirements, ensuring an optimal fit and functionality.
3. Boosted Reliability
Wiring Errors Become a Thing of the Past
Swapping out conventional cable harnesses for busbars eliminates the potential for miss-wiring. Considering the significant failure rates of wiring harnesses, busbars offer a virtually error-free alternative.
4. Enhanced Electrical Performance
Superior Capacitance
Laminated busbars enhance capacitance, leading to a drop in characteristic impedance. This equates to signal suppression and noise elimination better.
Reduced Inductance and Impedance
Busbars, designed with thin parallel conductors and a slender dielectric, significantly diminish inductance’s effects. This design also ensures a coveted low impedance, further refining the electrical performance.
5. Compact Design for Denser Packaging
The incorporation of wide, thin conductors in busbars leads to a reduction in spatial requirements. This compact design not only curtails system size but also trims system costs.
6. Versatile Interconnection Methods
Busbars boast a plethora of interconnection styles. Whether bushings, embossments, faston® tabs, wire harnesses, or solderable connectors, there’s a solution to interface with virtually any system.
7. Optimized Thermal Characteristics
As electrical systems miniaturize, heat dissipation becomes challenging and costly. The sleek design of busbars condenses system packaging and promotes better airflow, addressing the heat issue effectively.
Tips and Precautions
Selecting the Ideal Busbar: One of the foundational steps is to pick the right busbar tailored to your needs. This choice hinges on the application’s voltage, current, and frequency demands.
Installation Nuances: Remember, it’s not just about mounting the busbar but doing it right. Using the appropriate fasteners is crucial. Overzealous tightening might compromise the busbar’s integrity. A torque wrench, calibrated to the busbar machine manufacturer‘s specs, is your best bet to strike the right balance.
Safety First with Insulation: A properly insulated busbar minimizes risks such as electrical shocks and unintended short circuits. While at it, always sport personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety goggles, gloves, and attire with long sleeves.
Clear Markings: Labeling can’t be stressed enough. Marking the busbar not only aids in its identification but also underscores its specific function.
Regular Check-ups: Regular visual inspections can head off potential problems. Be on the lookout for any wear or damage.
Overloading and Bending – Just Don’t: It might seem tempting, but avoid overburdening the busbar. This might lead to overheating or even a meltdown. As for bending, stick to the manufacturer’s recommended radius. Going beyond this can weaken the busbar, impacting its efficacy.
It’s Not a Ground or Support: The busbar isn’t crafted to act as a ground conductor or bear weight. Using it as such is inviting trouble.
Stay Updated and Educated: Busbars might appear simple, but working with them carries inherent risks due to their high voltage and current potential. It’s paramount to peruse the manufacturer’s guidelines. And if in doubt, a chat with an electrical engineer or a seasoned electrician can dispel any uncertainties.
Conclusion
Whether setting up a new electrical system or optimizing an existing one, understanding the role of busbars is crucial. They not only promote efficiency but also bolster safety and reliability. While the decision to use a busbar should ideally be based on technical requirements and expert consultations, having foundational knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions. If in doubt, always lean on the expertise of a qualified electrician.