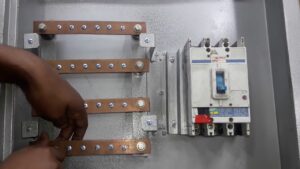
Busbars are ubiquitous in electrical engineering, used to conduct high currents safely and efficiently between equipment. But why are they typically rectangular rather than round?
As a professional busbar machine manufacturer, I’ve done extensive research into the design considerations behind busbar shapes. In this comprehensive guide, I’ll share key reasons why rectangular busbars have become the dominant standard.

Why Busbar is Commonly Rectangular
Rectangular busbars are favored due to superior performance in several areas crucial for safe, reliable electrical distribution. This includes:
- Higher current capacity
- Enhanced heat dissipation
- Greater mechanical stability
- Ease of manufacture and assembly
- More efficient use of space
Understanding these technical factors sheds light on why the rectangular form prevails over other busbar shapes in modern systems.
How Busbars Distribute Large Electrical Currents
Before getting into the advantages of rectangular busbars, it’s helpful to understand busbars’ role in electrical systems.
Busbars conduct electricity between major components in power distribution systems and industrial equipment. Rather than use individual wires, busbars offer a convenient centralized “bus” to carry huge currents.
Typical applications include:
- Switchgear
- Motor control centers
- Large transformers
- Electric vehicle charging systems
Proper busbar design is crucial for operational safety and performance. Rectangular busbars provide distinct advantages for these heavy-current applications.
Key Benefits of Rectangular Busbars
Now let’s explore the top reasons rectangular busbars dominate electrical engineering landscapes:
1. Higher Current Capacity
Rectangular busbars have a larger surface area compared to circular bars of equivalent cross-sectional area. This increased surface area is key to handling higher currents without overheating.
Why does this shape provide better cooling?
First, more surface area allows more heat dissipation from the conductor to the surrounding air. Second, the sharp edges on rectangular busbars enhance this heat transfer rate even further through a phenomenon called “edge effect”.
Together, these effects enable rectangular busbars to carry more current without exceeding temperature rise limits. Excess heat is dangerous for conductors and nearby equipment.
2. Enhanced Mechanical Stability
The flat, rigid edges of rectangular busbars also provide superior mechanical stability compared to round conductors:
- Easier to mount securely on bus supports
- Maintains spacing between bus phases with insulators
- Withstands short circuit forces and vibration better
This stability ensures critical clearances between current-carrying busbars and grounded equipment are maintained.
3. Simpler Manufacturing and Installation
Rectangular busbars involve cheaper, simpler fabrication processes like punching, drilling, and bending versus extruding round conductors. This saves costs in mass production.
The flat shape also makes installation easier in crowded electrical rooms and switchgear lineups. Multiple busbars can be neatly lined up and spaced with insulators.
4. More Efficient Use of Space
Electrical switchgear rooms and busways must house many other components besides busbars.
The rectangular shape allows compact, orderly arrangement in these tight spaces while maintaining safe isolation distances. Circular bus would waste room left between round surfaces and electrical clearances.
5. Flexible Power Tapping
Rigid, rectangular busbars enable convenient tapping of power all along their length to supply equipment. Built-in holes spaced along bus lengths or specialized tap boxes simplify connections.
Round bus is far less accommodating to taps without intricate busbar shaping.
When Circular Busbars Work Better
While rectangular bus reigns supreme for typical usage, round busbars still shine in certain applications:
- Extreme mechanical stresses require circular’s flexibility
- High-voltage direct current (HVDC) systems due to lower inductance
- Applications requiring many bends or special shaping
So for specialized needs, don’t rule out round busbars!
Conclusion
Rectangular busbars offer significant performance and practical advantages that make them a staple of electrical distribution systems where reliable high-capacity power distribution is paramount.
Their excellent thermal properties, mechanical rigidity, safety, manufacturability, and compact form underpin rectangular busbars’ dominance. While round bus fills some niche applications, rectangular busbars will continue electrifying industrial facilities for years to come.
Understanding these pragmatic electrical engineering design choices sheds light on the reasoning behind rectangular busbars’ success.